Build methods
Table of contents
1. Introduction
2. Changing build method
3. Configuring and creating new build methods
3.1 Overview
3.2 Creating
3.3 Configuring
3.3.1 Builder
3.3.2 C/C++ build methods
3.3.3 Android build method
4. Build method file format
5. Special variables
1. Introduction
Build methods define how TheIDE and UMK compiles and builds a concrete project. Each build method can be configured in a dedicated settings window, and you can create multiple build methods - each with its own independent configuration.
In each configuration, you can specify various options such as the compiler name, compilation flags, and build type (Release or Debug).
Together with packages, build methods lie at the very heart of the U++ build system.
2. Changing build method
To change the build method, click the left arrow next to the control where the current build method is displayed. This is illustrated in the image below:
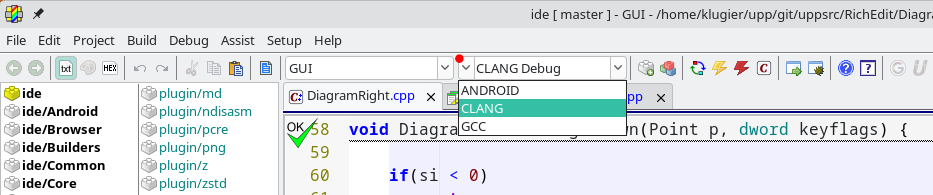
The right arrow is used to switch the build method mode. You can choose between Debug and Release builds.
3. Configuring and creating new build methods
3.1 Overview
To configure or add new build methods, open the Build Methods configuration window. To do this, go to the main TheIDE menu bar, select Setup, and then choose Build Methods... If you have trouble finding these options, refer to the image below, which shows the exact menu items to select.
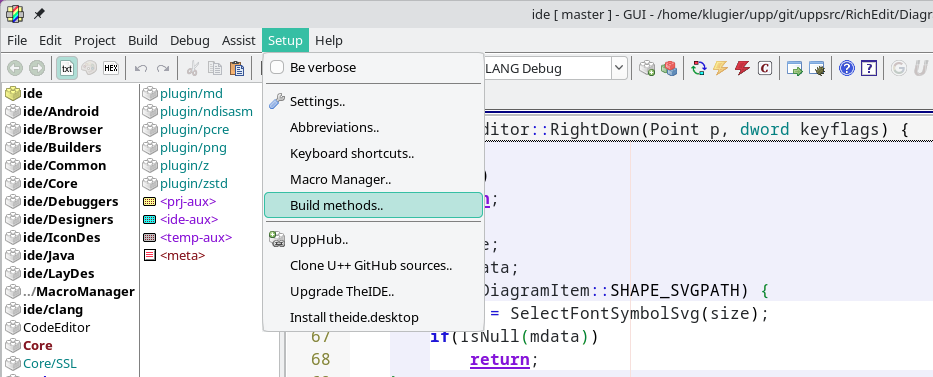
3.2 Creating
To add and create a new build method, right-click on the Method list and select Append row, as shown in the image below.
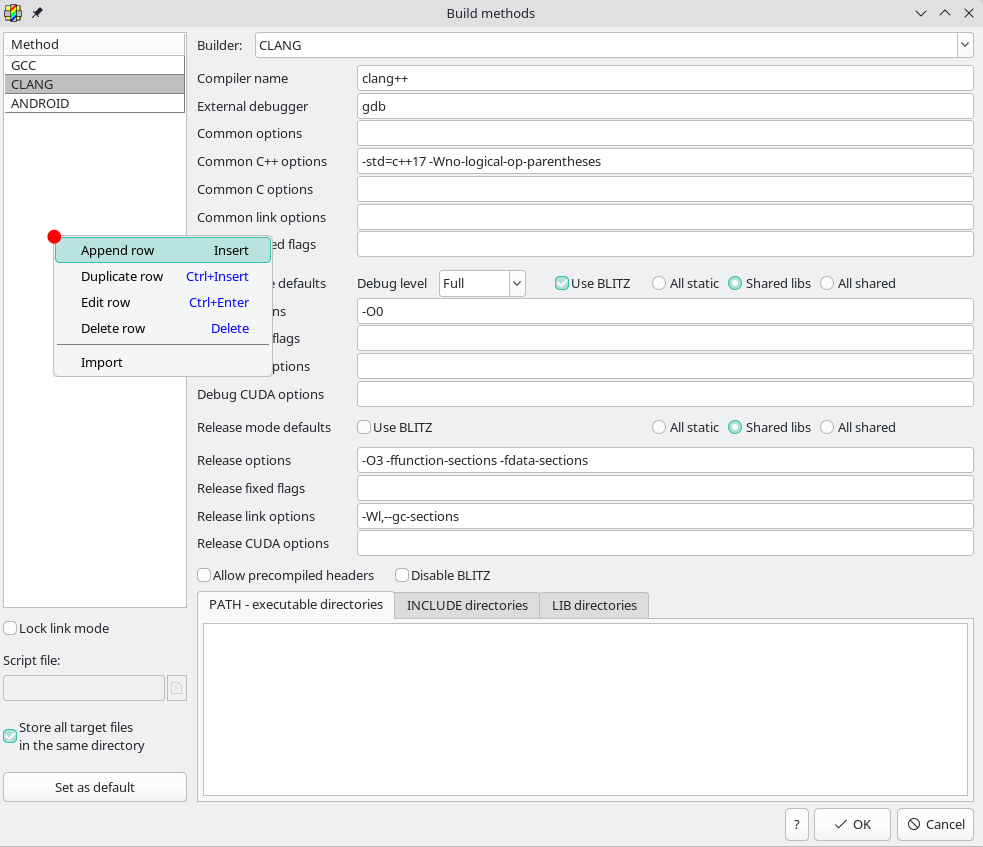
Once the new build method has been added, specify a name for it and adjust its configuration accordingly.
3.3 Configuring
3.3.1 Builder
After creating a new method, a blank window will appear. This window contains only one option: Builder, which determines the type of build method. The options you can choose from are:
GCC - method that utilizing g++ compiler
CLANG - method that utilizing clang compiler
MSVC* - method dedicated to Microsoft Visual C compiler, each major version has separate builder
Android - method dedicated to Android
3.3.2 C/C++ build methods
The default build method type used for development in TheIDE and the U++ framework is C/C++. This type includes the GCC, CLANG, and MSVC* builders, which have the same configuration options. The configuration options are:
General options
Compiler name - The compiler executable file name.
External debugger - The debugger executable file name.
Common options - Common compiler options for both C and C++.
Common C++ options - Compiler options for C++ language files.
Common C options - Compiler options for C language files.
Common link options - Linker options.
Common fixed flags
Debug build options
Debug level - The amount of debug information generated by the compiler. Options are:
None
Minimal
Full
Use BLITZ - if enable packages are being compiled in Single Compilation Unit (SCU) mode for the debug build. This setting is used to significantly decrease compilation time.
Libraries linking mode - Determines the mechanism by which external libraries are incorporated into the final executable for the debug build. Options are:
All static - All components, including project packages and system libraries, are linked statically.
Shared libs - Project packages are linked statically, while system libraries are linked dynamically.
All shared - All components, including project packages and system libraries, are linked dynamically.
Debug options - Compiler options for debug build.
Debug fixed flags
Debug link options - Linker options for the debug build.
Release build options
Use BLITZ - If enabled, packages are compiled in Single Compilation Unit (SCU) mode for the release build. This setting is used to significantly decrease compilation time.
Libraries linking mode - Determines the mechanism by which external libraries are incorporated into the final executable for the debug build. Options are:
All static - All components, including project packages and system libraries, are linked statically.
Shared libs - Project packages are linked statically, while system libraries are linked dynamically.
All shared - All components, including project packages and system libraries, are linked dynamically.
Release options - Compiler options for the release build.
Release fixed flags
Release link options - Linker options for the release build.
3.3.3 Android build method
The Android build method provides a different set of options compared to the standard C/C++ build methods. Under the hood, it functions more like a package builder than a simple compiler wrapper.
The Android build method includes the following parameters:
Executable Paths
JDK Path - the path to the Java Development Kit installation.
Android SDK Path - the path to the Android Software Development Kit installation.
Android NDK Path - the file path to the Android Native Development Kit installation.
Android SDK settings
Platform version - Specifies the Android API Level (e.g., API 36 for Android 16) that your application will be compiled against. This determines the set of APIs and features available to your code.
Build tools version - Specifies the version of the command-line utilities (like aapt, dx, zipalign) used to build the Android package (APK or AAB).
Android NDK settings
Use BLITZ - If enabled, packages are compiled in Single Compilation Unit (SCU) mode for the release build. This setting is used to significantly decrease compilation time.
Target architecture - Specifies the target architectures for compiling native source files. If the selected architectures do not match the Android device's CPU, the application will not run. Options are
armeabi-v7a
arm64-v8a
x86
x86-64
Toolchain
C++ runtime
Common C++ options - Compiler options for C++ language files.
Common C options - Compiler options for C language files.
For more information, see the article on the Android Builder.
4. Build method file format
On disk, a build method is represented as a text file, with each method stored in a separate file using the .bm (build method) extension. These files contain exactly the same information shown in the UI. There are no hidden or undocumented options. The contents of the file vary depending on the build method type. For example, C/C++ methods differ from Android methods.
Exemplary .bm file content for the C/C++ build method:
BUILDER = "CLANG";
COMPILER = "clang++";
COMMON_OPTIONS = "";
COMMON_CPP_OPTIONS = "-std=c++17 -Wno-logical-op-parentheses";
COMMON_C_OPTIONS = "";
COMMON_LINK = "";
COMMON_FLAGS = "";
DEBUG_INFO = "2";
DEBUG_BLITZ = "1";
DEBUG_LINKMODE = "1";
DEBUG_OPTIONS = "-O0";
DEBUG_FLAGS = "";
DEBUG_LINK = "";
RELEASE_BLITZ = "1";
RELEASE_LINKMODE = "1";
RELEASE_OPTIONS = "-O3 -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections";
RELEASE_FLAGS = "";
RELEASE_LINK = "-Wl,--gc-sections";
DEBUGGER = "gdb";
ALLOW_PRECOMPILED_HEADERS = "0";
DISABLE_BLITZ = "0";
PATH = "/home/klugier/7z;/home/klugier/just";
INCLUDE = "";
LIB = "";
LINKMODE_LOCK = "0";
5. Special variables
Build methods supports special string that can be treated as special variable. These strings are preprocessed by TheIDE and UMK once running the build. The special variables are:
${METHOD_DIR} - Replaces the specified string with the full path to the directory containing the build method file. This applies to the PATH, INCLUDE, and LIB configuration options, and is useful when the build method is bundled with the UMK distribution. Such distributions are primarily intended for building U++ framework applications from the terminal, excluding TheIDE.
|
